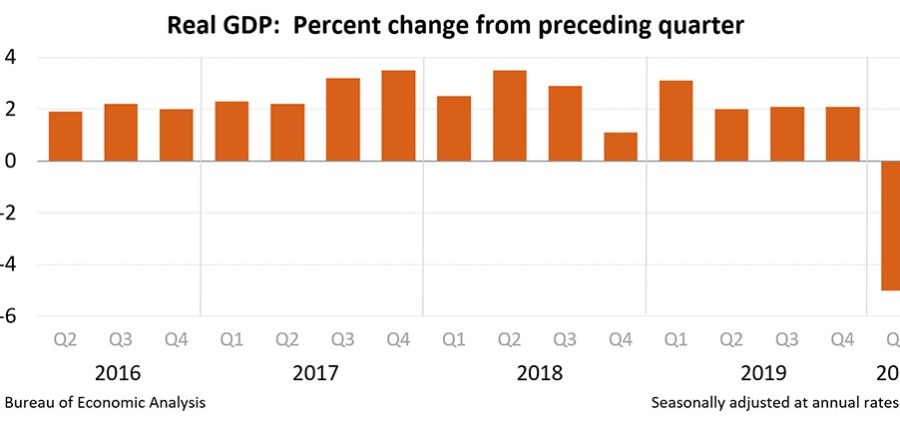
Real gross domestic product (GDP) decreased at an annual rate of 5 percent in the first quarter of 2020, according to the “third” estimate released Thursday by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. In the fourth quarter, real GDP increased 2.1 percent.
The GDP estimate released Thursday was based on more complete source data than were available for the “second” estimate issued last month. In the second estimate, the decrease in real GDP was also 5 percent. With the third estimate, an upward revision to nonresidential fixed investment was offset by downward revisions to private inventory investment, personal consumption expenditures (PCE) and exports.
The decline in first quarter GDP reflected the response to the spread of COVID-19, as governments issued “stay-at-home” orders in March. This led to rapid changes in demand, as businesses and schools switched to remote work or canceled operations, and consumers canceled, restricted, or redirected their spending. The full economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be quantified in the GDP estimate for the first quarter of 2020 because the impacts are generally embedded in source data and cannot be separately identified. For more information, see the Technical Note.
The decrease in real GDP in the first quarter reflected negative contributions from PCE, private inventory investment, exports and nonresidential fixed investment that were partly offset by positive contributions from residential fixed investment, federal government spending, and state and local government spending. Imports, which are a subtraction in the calculation of GDP, decreased.
The decrease in PCE reflected a decrease in services, led by health care as well as food services and accommodations. The decrease in private inventory investment was mainly in manufacturing, led by petroleum and coal products. The decrease in exports primarily reflected a decrease in services, led by travel. The decrease in nonresidential fixed investment primarily reflected a decrease in equipment, led by transportation equipment.
Real gross domestic income (GDI) decreased 4.4 percent in the first quarter, in contrast to an increase of 3.1 percent in the fourth quarter. The average of real GDP and real GDI, a supplemental measure of U.S. economic activity that equally weights GDP and GDI, decreased 4.7 percent in the first quarter, in contrast to an increase of 2.6 percent in the fourth quarter.
Current dollar GDP decreased 3.4 percent, or $189.4 billion, in the first quarter to a level of $21.54 trillion. In the fourth quarter, GDP increased 3.5 percent, or $186.6 billion.
The price index for gross domestic purchases increased 1.7 percent in the first quarter, compared with an increase of 1.4 percent in the fourth quarter (table 4). The PCE price index increased 1.3 percent, compared with an increase of 1.4 percent. Excluding food and energy prices, the PCE price index increased 1.7 percent, compared with an increase of 1.3 percent.